12. Toolbar#
The Polaris toolbar gives access to only a few tools, but some of them can only be accessed through the bar itself.

12.1. File level#
 Gives access to the creation of new Polaris files where the user is
able to choose a projection system adequate for their modeled area.
Gives access to the creation of new Polaris files where the user is
able to choose a projection system adequate for their modeled area.
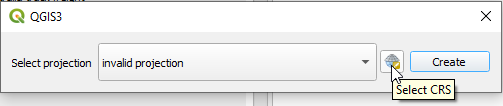
Using the CRS selector is straightforward and using the filter option (shown below ) is advised if you are going to choose a project CRS at the time of the project’s creation.
Please note that Polaris only supports file systems projected in meters.
 Is a shortcut to opening a Polaris Supply files.
Is a shortcut to opening a Polaris Supply files.
 Is a shortcut to opening the Polaris QGIS Plugin help, shipped
with the software
Is a shortcut to opening the Polaris QGIS Plugin help, shipped
with the software
 Is a shortcut to opening the current Polaris project on Windows
explorer or equivalent.
Is a shortcut to opening the current Polaris project on Windows
explorer or equivalent.
12.2. Model maintenance#
12.2.1. Database Upgrading#
 Upgrades Supply and Demand databases that have been loaded. It requires
that these demand and supply databases have been created after sometime in the
first semester of 2022, when the current database upgrading strategy was
adopted.
Upgrades Supply and Demand databases that have been loaded. It requires
that these demand and supply databases have been created after sometime in the
first semester of 2022, when the current database upgrading strategy was
adopted.
12.2.2. Network checker#
 Opens the Polaris network error checker, below
Opens the Polaris network error checker, below
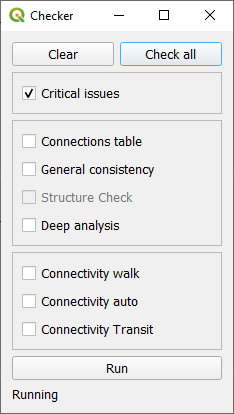
The network checker gives access to a number of verification tools that can be useful when editing the network, as the user can identify errors likely to crash Polaris before it happens. It is recommended that the user would run the critical check test after editing the network and before running Polaris.
Results of the checks will be loaded into a report screen and written down to the logfile.
A video demonstration of the network checker can be found in the video below, which also includes a demonstration of the network diagnostics tool.

12.2.3. Consistency enforcer#
 Is a shortcut to running the Supply consistency enforcer. Most editing
tools in QGIS would automatically trigger the consistency enforcer, but it is
recommended that you run it after editing the network to ensure that the network
is internally consistent.
Is a shortcut to running the Supply consistency enforcer. Most editing
tools in QGIS would automatically trigger the consistency enforcer, but it is
recommended that you run it after editing the network to ensure that the network
is internally consistent.
12.2.4. Polaris log File#
The POLARIS network log file is shared between the Python package and the QGIS
plugin and the Python library, and lives in your temp folder under the name
polarisnetwork.log. Although you can navigate to it in your file system and opening
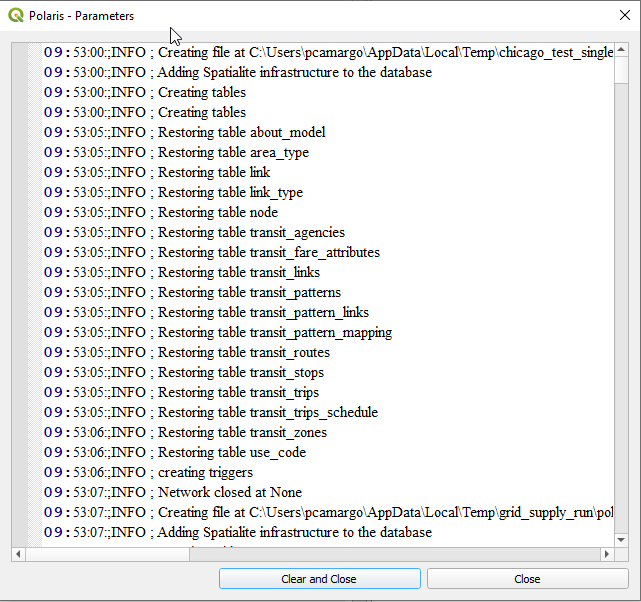
it on your favorite text file editor or log file viewer, selecting the log file.
 icon from the toolbar gives you a graphical interface where you can explore
the log file, copy out to your clipboard or clear it completely, as shown below:
icon from the toolbar gives you a graphical interface where you can explore
the log file, copy out to your clipboard or clear it completely, as shown below:
12.3. Location explorer#
Gives access to the location explorer, a tool designed to allow the user to
visualize data from the Location_Links, Location_Parking and EV_Charging_Stations
tables. Since the first two tables are not geo-enabled, the plugin will select all their records
corresponding to the location being visualized and highlight them in the Links and Parking
layers respectively.
It is important to note that the explorer is not designed to generate report-ready maps, but rather make it easier to visualize the data clearly and quickly. To that effect, the user can type the ID the location they want to visualize in the tool’s GUI, or just click on the location they want to visualize.
The use of the tool is exemplified below.
12.4. Traffic#
 Is a shortcut to the intersection explorer tool and its functionality
is explained in Exploring and Editing Intersections.
Is a shortcut to the intersection explorer tool and its functionality
is explained in Exploring and Editing Intersections.
 Clears the intersection exploration components from the workspace
Clears the intersection exploration components from the workspace
12.5. Network editing#
 Tool for cutting a link. Explained further in Breaking links.
Tool for cutting a link. Explained further in Breaking links.
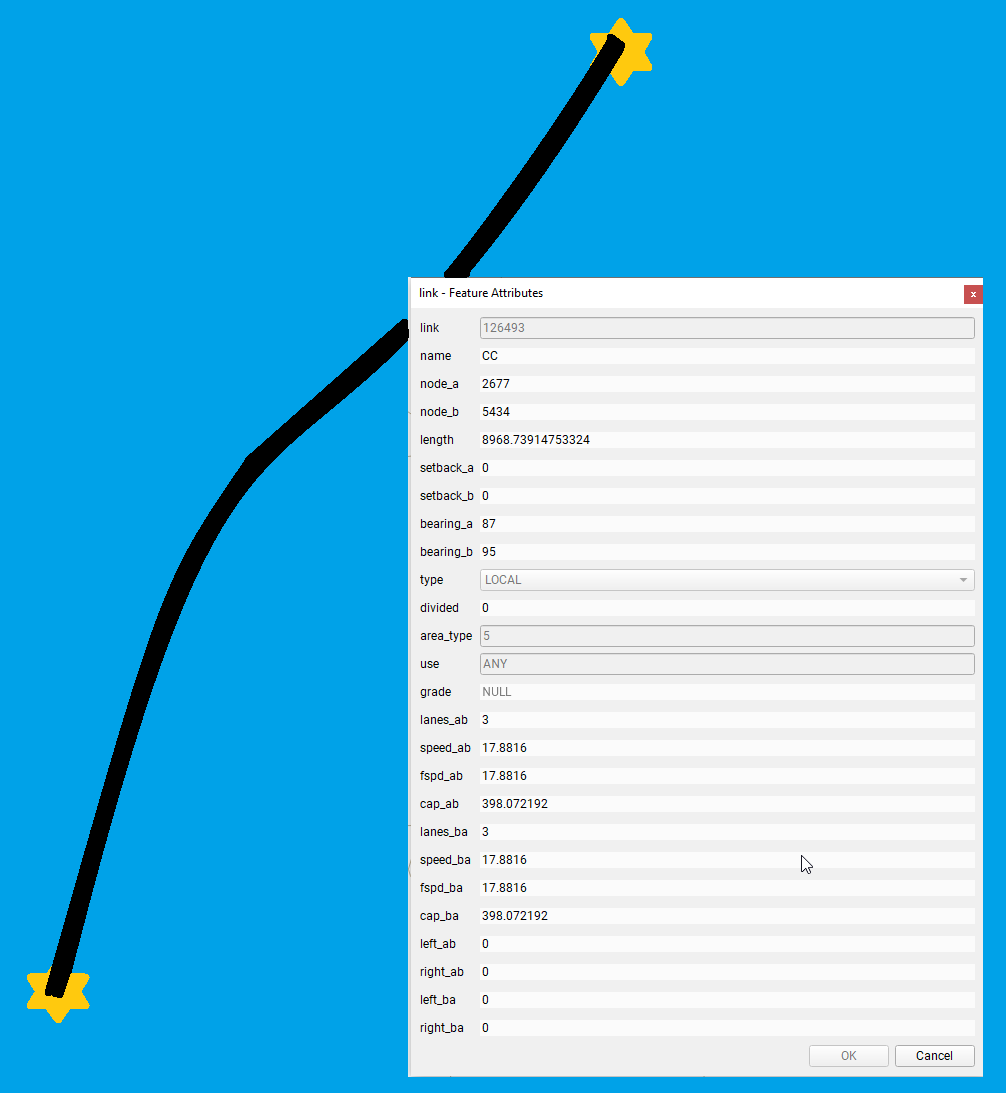 Tool for creating a link using an existing link as template. Explained
further in New link with template.
Tool for creating a link using an existing link as template. Explained
further in New link with template.
Tool for inverting the directionality (topology) of selected links. It INSTANTLY
reverts the topology of ALL SELECTED LINKS. Use with caution. Link Layer must be in editing model.